If the soul lives in evil, it dies (abbreviated). The soul becomes evil when it retreats from God, It becomes righteous by advancing towards God". Augustine, Reading from the Gospel of John. 19
Introduction.
Hans Christian Andersen is one of my favourite writers, although there was a period in the 80s and 90s when a lot of interpretative books were published that were too biased towards Freudian psychology, but even Freud was used in a superficial way and analysed in a ‘this is the real Andersen’ way, which was disturbing to me as a young child. He was ahead of Freud and pre-Jungian psychology in terms of the soul’s preference for sanctity, although for him there was a natural hatred of women and a contradiction in the soul’s attempt to approach God as a Christian. As I grew older, I may have gone through the four seasons of life. Spring, summer, autumn, winter and again in the milder seasons when he could see the traces of his soul. I believe that Andersen was blessed by God and left something important for us as Christians. In this article I will focus on The Little Mermaid and critique what I felt certain about, comparing my analysis with Andersen’s autobiography.
Ⅰ My Pilgrim’s Progress is a beautiful story.
How does one perceive God when misfortune strikes? Does it make you angry that you don’t believe in God, or do you seek salvation from God – Hans Christian Andersen was neither. There is a fairy-tale purification or sublimation in Andersen’s work, as if misery were a stage for the soul. His style as such did not drown out the Jesus-like love in the picture books sold in Japan, even when the Christian elements were removed. The characters’ actions and love are often accompanied by self-sacrifice. As a child I wondered why kind feelings were so beautiful. The world he radiated was beautiful, even if it was accompanied by pain and poverty.
Andersen’s life was not privileged. Not only was he poor, but his grandfather was a stereotypical schizophrenic and his grandmother a pathological liar. We don’t know who his father was, and as for his mother, she had a bad attitude and bad masculine habits. He was torn between loving his mother and despising her. Andersen had a fantasy wall about his grandmother. When his classmates mocked him for being poor, he would reply that he was really a child of the nobility and that an angel of God would come down to talk to him.
Otherwise, the friendship would not have worked. If the stories of unhappiness are true, it is also a terrible way to introduce himself. For a child from such a background, it becomes a story about the family rather than an introduction to oneself. If I am a ‘phenomenon’ made up of nature and the lives of several people, as Kenji Miyazawa sometimes described the ‘phenomenon of the I’ in his AN ASURA IN SPRING, then I am in the middle stage of the experience of the ‘I’, which is an undifferentiated state, leaving the essence itself to the inner world and not to the values of others. It is not that one is positioned by others as a ‘poor person’, but that one must believe that the essence is growing in order to stand. (We want to believe) Believing in the essence leads to believing that God loves you. Deep inside there is enough mystery to bring you closer to God, but when you are young you don’t even know what it is. If it is too early to talk about The Light, once a writer’s talent is there, he or she has to lie in order to remain socially relevant. Every child in such a situation knows whether it will be a flowery embellishment or a lie to get closer to mediocrity. In the first place, it is socially necessary to tell a comfortable story, rather than a background that only makes those around you uncomfortable, or to be thought of as a beggar. Making up stories may be a way for the mind to show its primordial ego. The fate of the ‘light’ story depends on what it protects from the things that hurt it early on.
Ⅱ have‐nots
Andersen seemed to understand best the ‘lies’ he told himself as a child. He knows that the poor cannot live otherwise, and yet he represents punishment without pardon. In The Red Shoes, the girl Karen went to buy Communion shoes, but kept cheating her adoptive mother, who had poor eyesight, by buying her splendid, beautiful red shoes. The girl forgot how much she owed her foster mother for raising her and started going to balls instead of looking after her. An angel put a ‘curse’ on Karen that made her dance all the time. Karen became tired and bitter because she could not stop dancing. She asks the official who beheads condemned prisoners to cut off her legs. Karen really does get her foot cut off. The story is said to reflect Andersen’s decision to live as a bachelor, but it also seems to be a reflection on his life. The girl cherished her red shoes, which were originally made from pieces put together. It was her adoptive mother who threw them away. Things that were cherished in childhood are indeed beautiful. Even if they were beautiful in nature, they must be punished for their mistakes. Even if you choose a beautiful red shoe as compensation for the most precious thing, it still represents the harshness of having cheated.
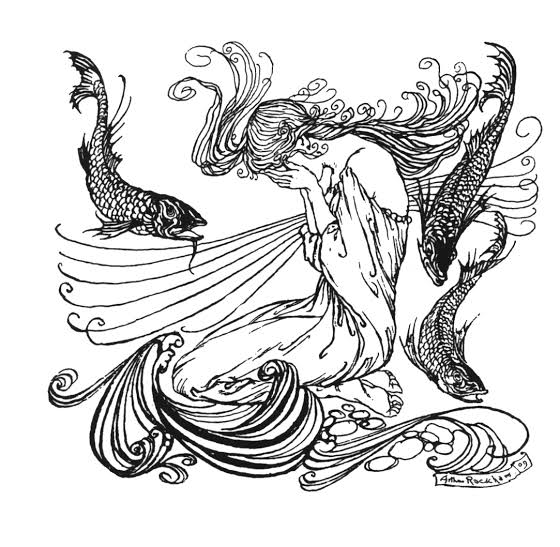
Although much of Andersen’s work deals with innate ‘destiny’ and self-sacrifice, it should also be noted that he lived and worked before the birth of Freud and Jungian psychology. Perhaps he would have known of Descartes’ ‘innate theory’. What would he have made of the idea that the idea of being born was already given to him by God because he was a ‘poor’ man with dysfunctional parents? Perhaps he was certain in his ‘heart’. Perhaps he was conscious enough to talk to God. However, as for that which cannot be divided by the innate theory, perhaps he had a desire to be changed by the ‘magic’ of a mermaid becoming a human being. Or it could be the belief that there is no way to change one’s identity without magic. Andersen had a beautiful singing voice and wanted to become an opera singer, but was frustrated by a voice change. Knowing this upbringing, many people will probably agree with the fact that the Little Mermaid loses her voice instead of becoming human. The Little Mermaid, a girl who lived an unconscious and given life in the water, trying to become a human adult in exchange for her voice, overlaps with Andersen’s childhood and the experience of being robbed of it in order to become an adult. For him, losing his voice was the same as becoming a “have-not”.
Ⅲ Temporary me and fate
His fairy tales do not use magic just for convenience; for him, his father was always the Lord, God. It is certain that for him, whose parents did not function, the teacher of good and evil was the Bible. All his works, like Augustinian theology, reflect the difference between what the soul gives to the body and what God gives to the soul.
。When will the transient ‘I’ become ‘Who’, and his fairy tales show the stages of this soul. Among them, ‘The Little Mermaid’ is a well-known love story, but it also represents the unworthiness and ‘poverty’ of human beings in relation to mermaids. It is a story like the sequel to Fouquet’s ‘Undine’, where Undine was given the sacrament of marriage by a priest, but the mermaid was not. The priest who administers the sacrament does not appear. Undine was betrothed to a being of status in the human world, and if the man broke the marriage promise, Undine had to kill him. The severity of the punishment for betrayal is also seen as a religious punishment. Similarly, the mermaid princess is under a spell to continue living as a human if she can marry a prince of status. Water nymphs like Undine represent the ‘place of absolute nothingness’ where water pre-existed in God’s creation in Genesis. She was born out of the imagination of an underwater world that was never written about. Undine had to kill her spouse, but the mermaid princess chose to disqualify herself even if she did not marry the prince.
The mermaid can see the human world on her 15th birthday, but each of her sisters has seen a different world. This is similar to how baptised Catholics see a different world as they go through the same stages. Alternatively, in Jungian terms, the water could be interpreted as the unconscious world. The soul of the mermaid princess learned to love like a human, but the price was too high. The mermaid princess was given human legs, but every time she walked she was in great pain. For Andersen, who had a string of broken hearts, it was impossible to write about the fulfilment of adult love, but the dynamic of love is accompanied by pain, and this is reflected in the reality of the transition from girl to adult as a fairy tale and in the Christian teaching of ‘those who enter the kingdom of heaven’. This may have included the desire for women to love themselves, but he sublimates this desire as a fairy tale.
As if the author had forgiven the world, the mermaid princess, a poor creature, is blessed by God at the end. Because the story was written for an innocent child to read, the author’s upbringing was removed. And It was written in a clear style and in a beautiful mermaid world. The prince mistakenly believes that another woman saved him, when in fact it was he who saved the prince. For an ordinary woman, the end of a love affair would have been a passing phase in her life, but as a mermaid’s ‘fate’, the time given to her transient self, who had changed her identity, was short. This meant that when her one-time love ended, her life would end. It was so cruel that the mermaid’s sisters made a deal with the witch that if she killed the prince, she could return to being a mermaid and was given a knife, but the mermaid could not kill him even if she was given the knife. The Little Mermaid could not kill the prince, but she did not end up in a bubble. In the original story there was a sequel: the Little Mermaid became a genie. The mermaid princess, now a genie, finally kisses the prince’s bride on the forehead and leaves. The mermaid princess is told by other spirits that if she does good deeds for 300 years, she will eventually receive a soul that will never die and be entrusted with the never-ending happiness of mankind. If she finds a child who reciprocates her parents’ love, the Mermaid Princess will shorten the time she has a human soul by one year, but for every bad child she encounters and tears to pieces, she will extend it by one year.
****
What did Andersen learn from his young, transient self? In Japan, picture books were stripped of Christian elements, so many stories of The Little Mermaid ended in bubbles. That in itself was nothing but pessimism. But only The Little Mermaid, illustrated by Makoto Takahashi, included the story of how God transformed her into the daughter of the wind. I read it as a child. If we were to replace it with a modern version and compare it to the real world, it could only be a tragedy. This is not a story about a little girl who thinks dying is beautiful. Happiness is also about acquiring material things too. A healthy body, social status, family, friends, lovers, they are a mixture of the material and the sacred and cannot be dualistic. On the contrary, happiness that only enriches the soul creates a cult. Rather, fairy tales exist to nourish the inner life in a fictional world. They are not there to provide something pragmatic for today and tomorrow. Andersen certainly knew the reality that the poor can only achieve happiness through ‘death’. He did not remove this complex of poverty from his autobiography.
He went from a ‘transient’ existence to being loved even abroad as a ‘lucky grace’ through his fairy tales, which, like his creations, had an underlying sacredness. Fairy tales are not meant to be put into practice immediately, even if there is a lesson to be learnt. Even the faintest memory brings us closer to the love of Christ in which the author walked. But that may be just before the entrance to heaven, which will appear when we realise it from the fairy tale. The poor will not be saved tomorrow, some days I want to be saved and some days I want to help others. Even if you reach out to them, some days it doesn’t work. Some days you do something good and it backfires and you are resented. Injustice is not always condemned immediately. The right thing is not fruitful. Sometimes prayers lose their substance because it gets harder and harder to pray for miracles every day. Yet there is a spark in the back of people’s minds that wants to talk to God. Surely everyone has it. How can you hear it, the happiness of acquaintance, gratitude and much joy? trying to find the light on the other side of the needle’s hole. (Matthew 19:16-30)
He lied to himself as a child that he was a noble being who could talk to angels, and he was honest enough to make even that a creation. He made no attempt to hide himself. Psychoanalysis would only be able to analyse the rough outlines of the author’s desires. That is why there are so many analyses of the resentment of a lost love. To return to the story of the Little Mermaid, the book is full of descriptive beauty that I did not recognise in the picture book. He must have travelled and loved the world.
Last Pilgrimage
He lied to himself as a child that he was a noble being who could talk to angels, and he was honest enough to make even that a creation. He made no attempt to hide himself. Psychoanalysis would only be able to analyse the rough outlines of the author’s desires. That is why there are so many analyses of the resentment of a lost love. To return to the story of the Little Mermaid, the book is full of descriptive beauty that I did not recognise in the picture book. He must have travelled and loved the world.
—-The mermaid lived in a sea as clear as crystal – far out to sea, where the water was as blue as the bluest cornflower. Don’t think it’s just a cold expanse of white sand at the bottom of the sea. There are strange trees and grasses, their stems and leaves swaying. Even the slightest movement of the water makes them sway as if they were alive. The fish, large and small, all swim swiftly between the branches, like just as birds flit about on land. —-From a world more dreamy than earthly, the mermaid princess chose love. Love makes us happy and makes us grow, if only temporarily. Even if love is not fruitful, it shows the value of loving. Why she was able to love the prince so much cannot be told. The story shows that no matter how hard it is on earth, you can love someone no matter what their status is.
Fairy tales take you to a place where no outside voices can reach you, like underwater. When we return to reality, we hope that our formed hearts will not be forgotten. ーfor children’s. Isn’t that why, at the end, he wrote that he wanted the mermaid’s soul to be good so that it could go to the kingdom of heaven?
There is no fairy tale where you can see the subtleties of the soul as well as in this one, where the soul breathes and wonders and wants. It made me think that the soul of a man who had faith was beautiful. In his case, it was not just soul worship. What I learned from him was to write with the belief that everyone has a heart that wants to talk to God. Despite knowing the cruel reality, the soul tries to approach God’s goodness. That is why the human heart knows goodness. He travelled a lot. It was probably a pilgrimage where the ‘I’, which for him was transitory, came to understand God. He was constantly broken in love, but he wrote about loving others in his fairy tales. He wrote about love when it should have been the most incredible thing. Isn’t that power? To bring out this pure feeling, we have to take them to the fairy tales. The love of family, of lovers and of agape, To teach ‘love’, to believe in love, to give love, because only human beings can do that. Jesus also needs people’s understanding and words. I used to want God to believe that I had light in my heart. That someone else had that heart too. It is not yet 300 years since The Little Mermaid was published. The Little Mermaid’s soul has not yet reached heaven. If she is good, her day will come a year earlier; if she is bad, her day will come a year later. This is the soul’s approach to God. ―― Light visible behind the eye of the needle, So If you want to tell many people, it is like sowing many seeds.
-----------
Links to other websites
My column (in Japanese).
… This time, I focused on The Little Mermaid. Andersen has other works that do not fit into this review, such as The Shadow, but I decided to focus on them in this second instalment. The first volume is here.
The Hole of the Needle (Matthew 19:16-30).
Andersen is a Protestant.